Chains explained
The chain is a traditional unit of length used mainly in surveying and land measurement. Originally standardized as the Gunter's chain, the chain remains significant in historical land records, surveying practice, and some legal descriptions of property.
Symbol
The common symbol for the chain is ch. Older texts may simply spell out "chain" or use surveyor shorthand.
Chain in Imperial and US customary units
| Unit | Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Mile | mi | 1 mile = 80 chains |
| Furlong | fur | 1 furlong = 10 chains |
| Chain (base unit) | ch | Gunter's chain = 66 feet = 22 yards = 4 rods |
| Rod (also pole or perch) | rd | 1 rod = 16.5 feet = 0.25 chain |
| Link | li | 1 link = 0.66 feet; 1 chain = 100 links |
Comparison with other unit systems
The chain belongs to the imperial/US customary family of units and is not part of the SI system. For metric comparison, 1 chain = 20.1168 meters. Modern surveying generally uses meters, but chains appear in legacy records and some regional practices.
Uses and practical applications
The chain is historically important in cadastral surveying, property deeds, land subdivision, and mapping. Today it is most often encountered in historical land documents, legal descriptions, and teaching about surveying history.
- Interpreting historical property deeds and boundary descriptions
- Cadastral surveying and land registry research
- Teaching surveying methods and history
- Converting legacy measurements to modern units
Instruments and measurement
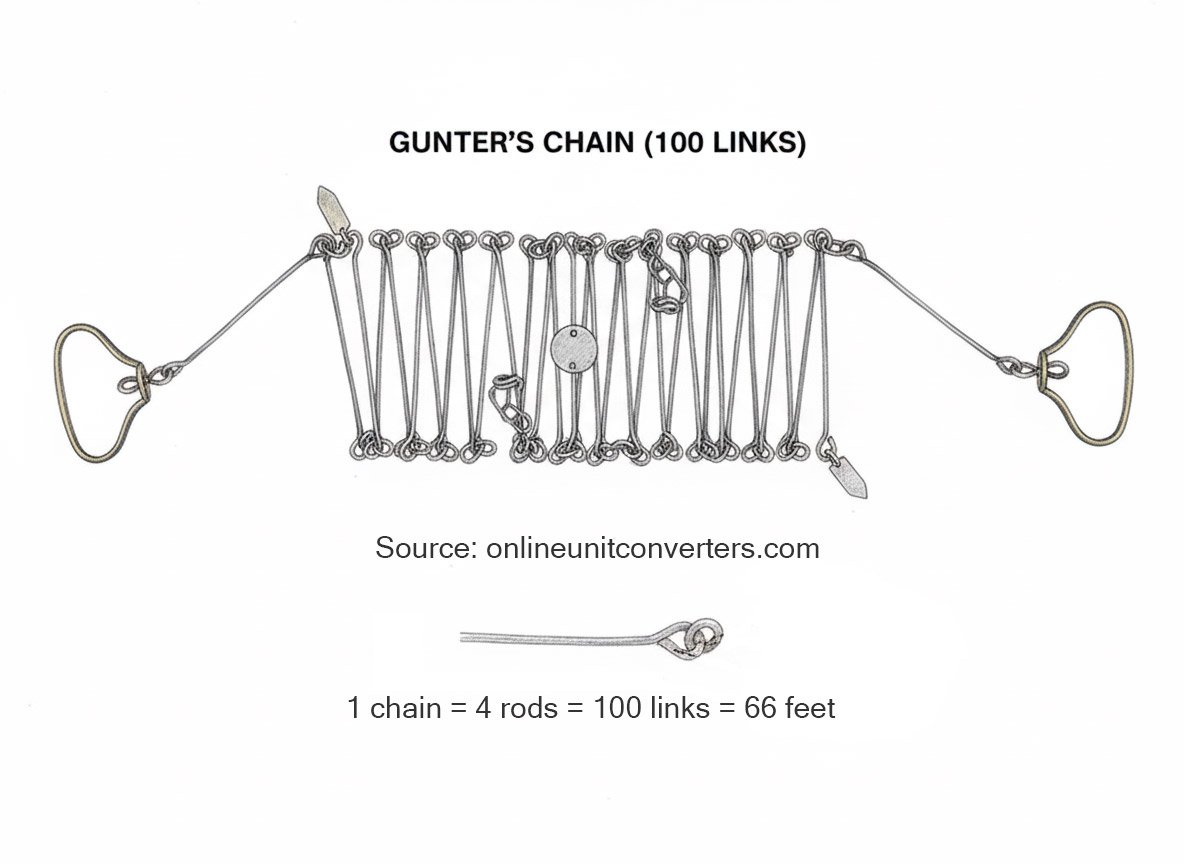
The original tool is the Gunter's chain (surveyor's chain), a physical chain of 100 links totaling 66 feet. Modern alternatives include steel survey tapes, total stations, and GNSS/GPS survey equipment that replace physical chains while preserving unit conversions.
Origin
The standardized surveying chain is attributed to Edmund Gunter, a 17th-century English mathematician and surveyor who introduced the Gunter's chain to simplify land measurement and calculation.
FAQs about the chain
Why is a surveying chain 66 feet long?
Gunter chose 66 feet because it divides evenly into common land-measurement units: 10 chains make a furlong and 80 chains make a statute mile. The length also yielded convenient relationships with acres (see next question).
How does the chain relate to acres?
One acre equals 10 square chains (an area one chain wide by ten chains long). This made area calculations straightforward when using the Gunter's chain in the field.
Is the chain still used for legal descriptions today?
Yes. Many older deeds and cadastral records use chains; surveyors convert those values to modern units when preparing new plans. Some jurisdictions still accept legacy descriptions that reference chains.
How long is a physical Gunter's chain and how is it constructed?
A Gunter's chain typically has 100 links and measures 66 feet in total. Links and rings are durable metal, and the chain often folds for transport. Specialized survey tapes and electronic equipment now replace it in practice.
Can I convert chains to meters or feet easily?
Yes. 1 chain = 66 feet = 20.1168 meters. Use that factor for precise conversions when translating historical measurements into metric units for mapping
How do I convert chains to other length units?
Use the links below for easy conversions from chains to other length units available on this website.
- Chains to meters
- Chains to kilometers
- Chains to hectometers
- Chains to dekameters
- Chains to decimeters
- Chains to centimeters
- Chains to millimeters
- Chains to miles
- Chains to yards
- Chains to feet
- Chains to inches
- Chains to light years
- Chains to astronomical units
- Chains to quettameters
- Chains to ronnameters
- Chains to yottameters
- Chains to zettameters
- Chains to exameters
- Chains to petameters
- Chains to terameters
- Chains to gigameters
- Chains to megameters
- Chains to micrometers
- Chains to nanometers
- Chains to picometers
- Chains to femtometers
- Chains to attometers
- Chains to zeptometers
- Chains to yoctometers
- Chains to rontometers
- Chains to quectometers
- Chains to microns
- Chains to megaparsecs
- Chains to kiloparsecs
- Chains to parsecs
- Chains to leagues
- Chains to leagues (uk)
- Chains to leagues (ancient celtic)
- Chains to nautical leagues (uk)
- Chains to nautical leagues (international)
- Chains to nautical miles (uk)
- Chains to nautical miles (international)
- Chains to miles (statute)
- Chains to miles (us survey)
- Chains to miles (roman)
- Chains to kiloyards
- Chains to furlongs
- Chains to furlongs (us survey)
- Chains to chains (us survey)
- Chains to ropes
- Chains to rods
- Chains to rods (us survey)
- Chains to perches
- Chains to poles
- Chains to fathoms
- Chains to fathoms (us survey)
- Chains to ells
- Chains to feet (us survey)
- Chains to links
- Chains to links (us survey)
- Chains to cubits (uk)
- Chains to hands
- Chains to spans (cloth)
- Chains to fingers (cloth)
- Chains to nails (cloth)
- Chains to inches (us survey)
- Chains to barleycorns
- Chains to mils
- Chains to microinches
- Chains to angstroms
- Chains to x units
- Chains to fermi
- Chains to arpents
- Chains to picas
- Chains to points
- Chains to twips
- Chains to alns
- Chains to famns
- Chains to calibers
- Chains to centiinches
- Chains to japanese kens
- Chains to russian archins
- Chains to roman actus
- Chains to spanish vara
- Chains to greek cubits
- Chains to long reeds
- Chains to reeds
- Chains to long cubits
- Chains to handbreadths
- Chains to fingerbreadths
- Chains to planck length
- Chains to classical electron radius
- Chains to bohr radius
- Chains to earth's equatorial radius
- Chains to earth's polar radius
- Chains to sun's radius





